- Feedback of wetland CH4 in projected future
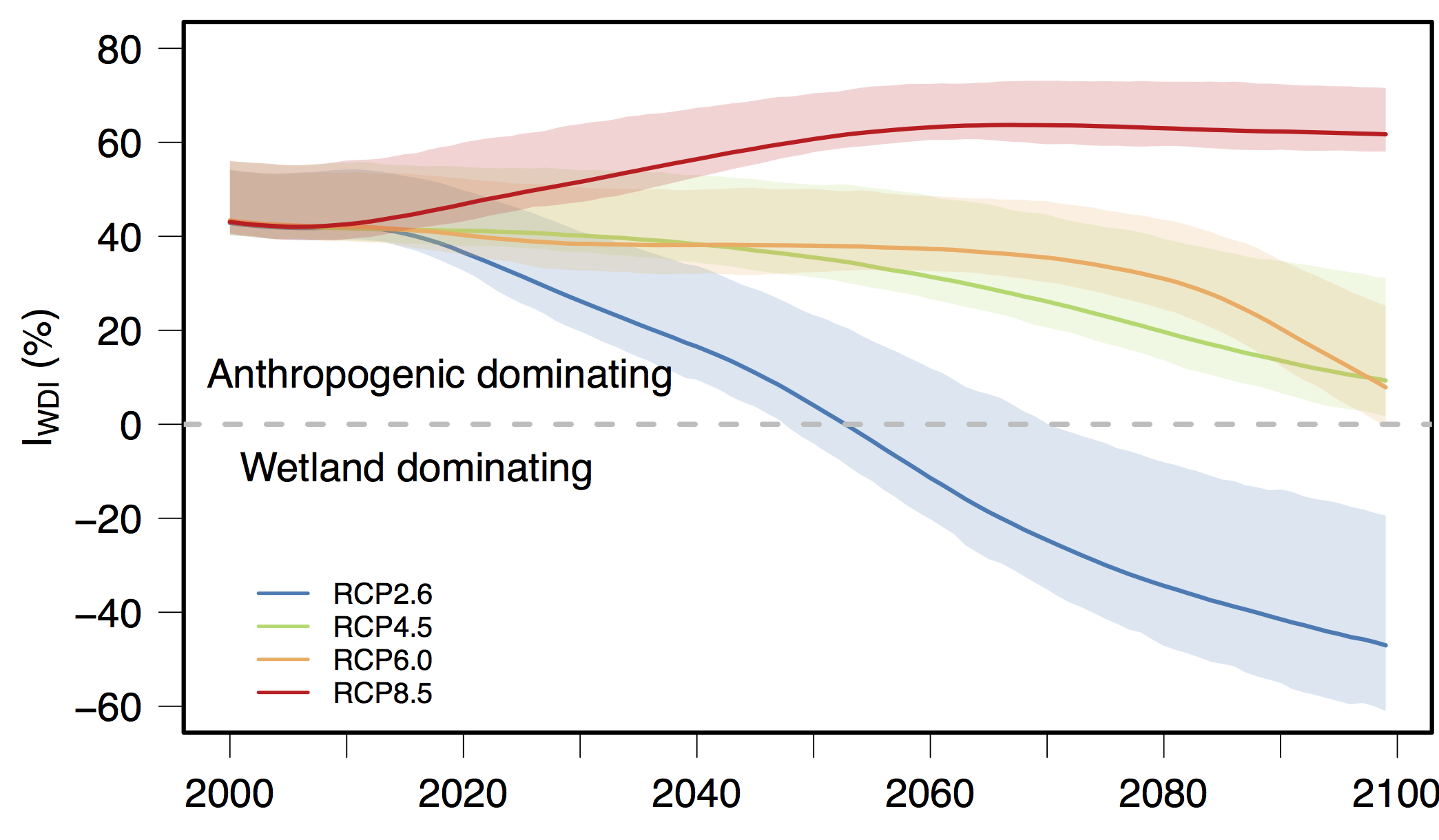
- Global Warming Potential caused by the response of wetland CH4 could overwhlem the anthropogenic CH4 emissions
Wetland CH4 feedback was assumed to be muted in the future climate scenarios in previous
climate projection. We use climate and vegetation models to provide a comprehensive
assessment and find that climate change could cause shifting dominances of global climate forcing
from anthropogenic to wetland CH4 emissions during the 21st century. Check out our recent publication on
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences for more details.
- Dynamics of global Wetland CH4 emissions
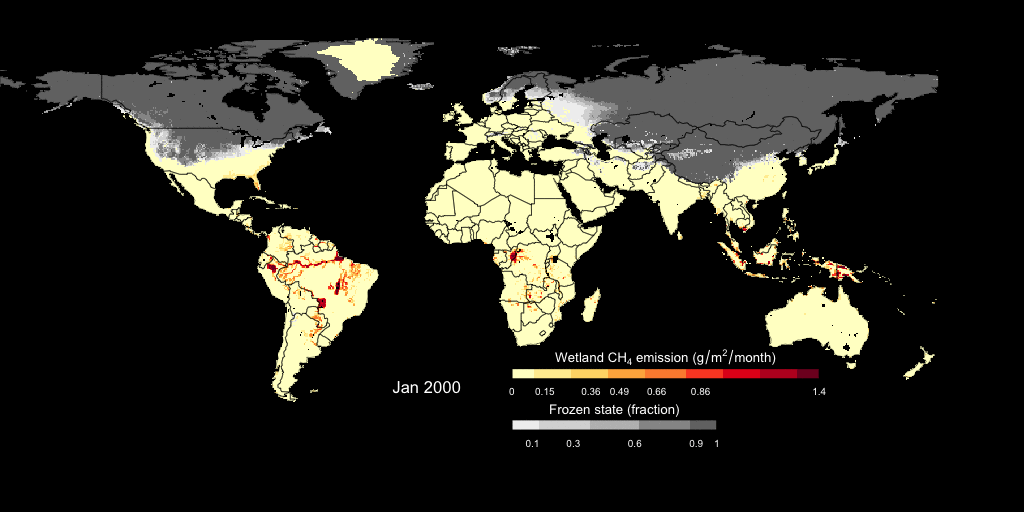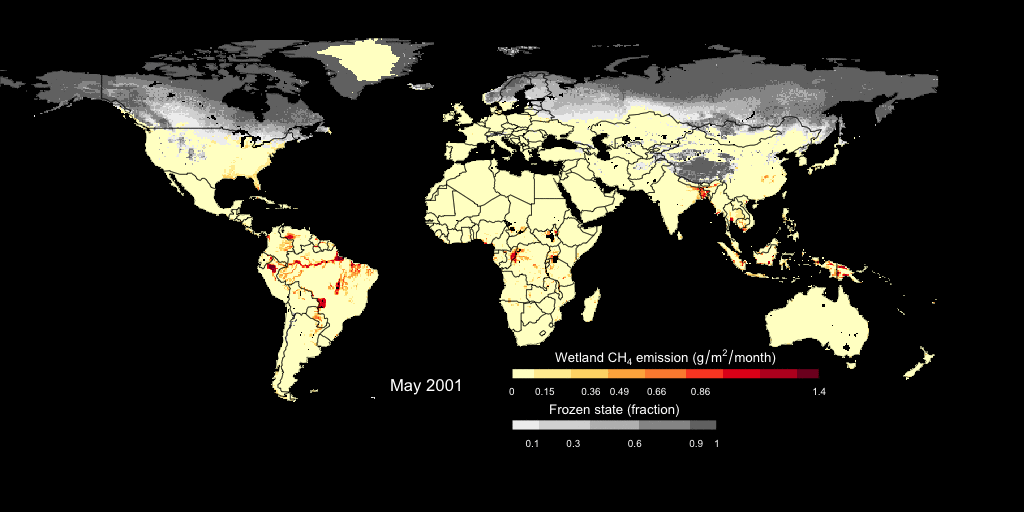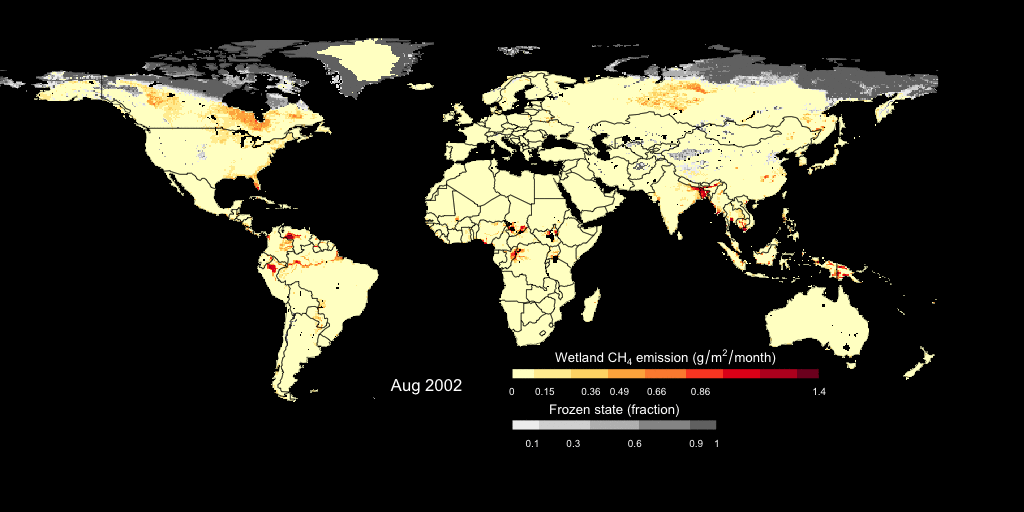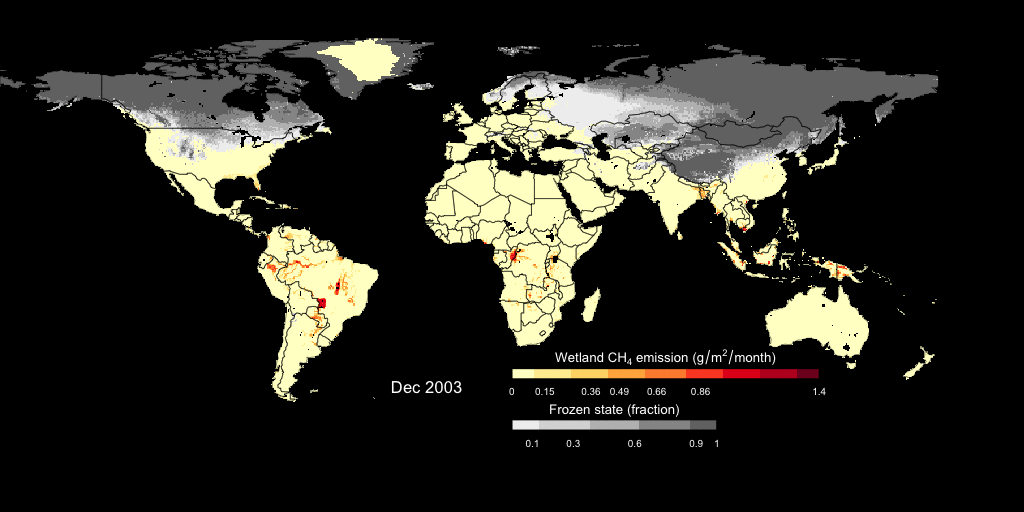
- wetland CH4 fluxes simulated by Dynamic Global Vegetation Model LPJ-wsl
This is an example showing the simulated monthly wetland CH4 fluxes and the freeze/thaw cycle. The wetland CH4 fluxes is estimated using a prognostic semi-empirical approach incorporated into LPJ-wsl model. Check out our paper on
Biogeosciences for more details.
- Wetland inundation dynamics
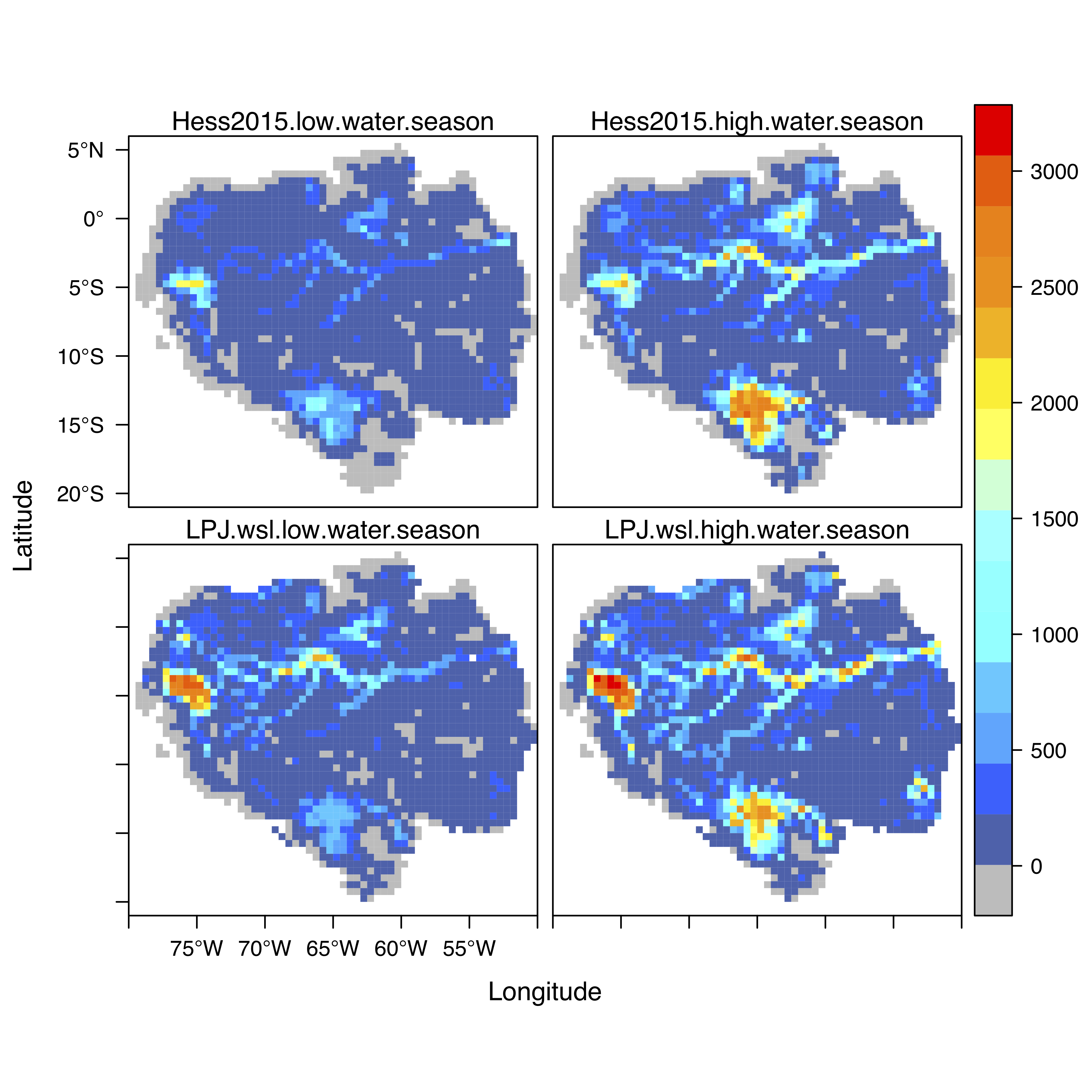
- Seasonal inundation simulated by LPJ-wsl in comparison with satellite JERS-1 (Hess et al., 2015) for Amazon regions.


